Lake Erie Hypoxia Forecast
The central basin of Lake Erie provides drinking water to more than 2 million people along the Ohio coast. In the summer, the lake stratifies, with warm water on the top and cold, dense, deep water below. Oxygen in this deep water is used up, resulting in low oxygen, or hypoxia. This hypoxic environment is typically inhospitable to many animals. The low oxygen water also has different chemistry from oxygenated water, which is problematic for the public water supply. Strong wind events in the summer can cause upwelling, which brings this cold, hypoxic bottom water up to the surface close to shore. This can cause a sudden degradation to the water quality at nearshore drinking water intakes. These events require rapid adjustments to the treatment process in order to maintain drinking water quality. As the upwelling events largely occur with an irregular frequency, local decision makers need timely warnings of the conditions that may cause them. This forecast uses a model of hypoxia and circulation in Lake Erie to alert decision makers of when upwelling may bring hypoxic water to the shore. The hypoxia forecast was developed by NOAA’s Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory, and is now being maintained by NCCOS. For our Lake Erie HAB forecast, click here.
Forecast Products
Localized hypoxic upwelling is possible from Sandusky to Huron. A narrow band of hypoxic waters (<2 mg L-1 dissolved oxygen) is located just offshore of the Ohio coast from Sandusky to east of Ashtabula. Southwesterly winds forecast through the weekend (July 11-14) decrease risk for most of the Ohio central basin coast. However, these winds increase risk for the Sandusky area through Monday. While the western basin does not typically have hypoxic events because winds tend to keep the shallow basin mixed, hypoxia has been occurring near the bottom in parts of the basin. Stronger winds Sat and Sunday should reduce hypoxia near the bottom, but light winds forecast Monday may increase risk for nearshore impacts in the western basin. This text will change if the risk changes. --Stumpf, 12 July 2025.
The Lake Erie Hypoxia Forecast is operated by the National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science.
Contact hab@noaa.gov for technical questions. Last Updated: 2025-07-14 08 AM EST
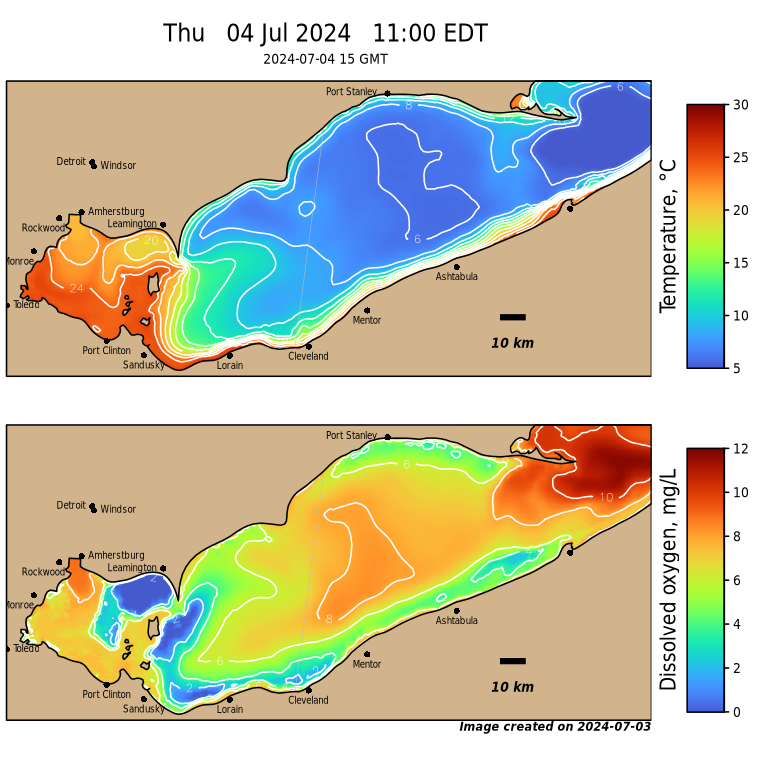
Forecasted Bottom Water Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen
Forecasted bottom water temperature and dissolved oxygen up to 5 days, based on coupled bio-physical model simulations for Lake Erie.
Please note, 10/22/2024 is the last model run for the 2024 forecast season.
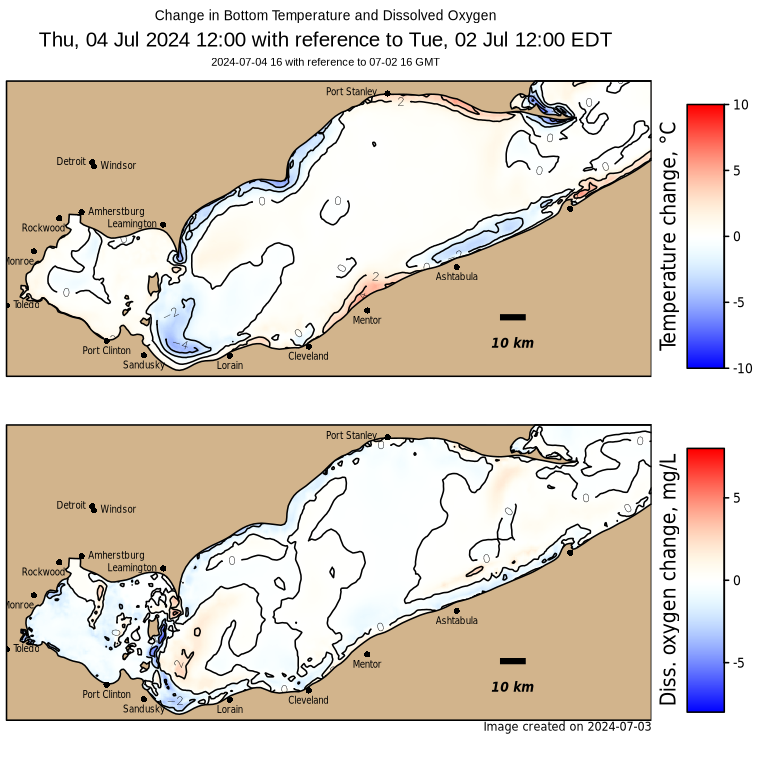
Forecasted Winds and Changes in Bottom Water Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen
Forecasted winds and changes in bottom water temperature and dissolved oxygen up to 5 days, based on coupled bio-physical model simulations for Lake Erie.
Please note, 10/22/2024 is the last model run for the 2024 forecast season.
