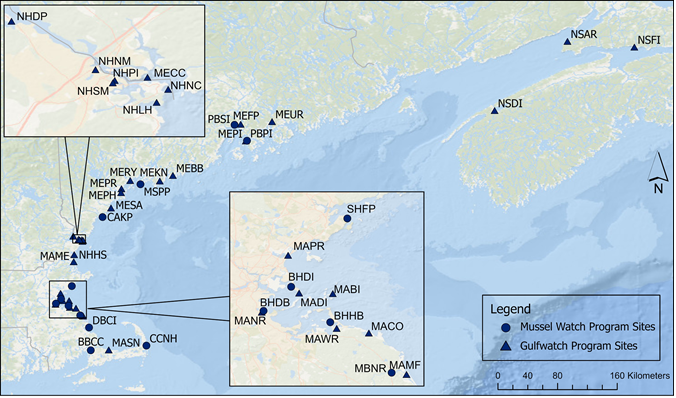
The Mussel Watch Program has monitored the nation’s coastal waters for chemical contaminants since 1986 and in recent decades has expanded its monitoring to include trace metals, legacy contaminants, and contaminants of emerging concern (CECs). In 2015–2016, the program collected mussel (Mytilus edulis) samples from a network of 41 sites in the Gulf of Maine. Results from this study will support a better understanding of the sources, fate, and transport of contaminants in the region and will fill important data gaps for local stakeholders.
Why We Care
The immense upwelling of nutrients and the combined productivity of seaweed, salt marsh grasses, and phytoplankton make the Gulf of Maine one of the world’s most productive ecosystems supporting a vast array of organisms, including some of great economic importance. Growing coastal populations combined with industrial and residential development have contributed contamination to the gulf through wastewater and industrial effluent discharges, septic system releases, and storm water runoff. Thousands of chemical contaminants from many land-based point and nonpoint sources accumulate in the Gulf of Maine every day, compromising water quality and, consequently, threatening human and ecosystem health.
Previous studies in the region have investigated legacy contaminants, such as trace elements and persistent organic pollutants (e.g., polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), organochlorine pesticides, chlordane, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)). These research and monitoring efforts have helped managers limit the impact that legacy contaminants have on coastal ecosystems, but such efforts are lacking for the increasing number of new and unregulated compounds known as contaminants of emerging concern (CECs), many of which are known to be harmful to people, animals, and the environment. In response to resource managers’ concerns about the extent and impact of these chemical stressors, the Mussel Watch Program conducted a basin-wide survey in 2015 and 2016 to assess the magnitude and distribution of a suite of CECs, metals, and legacy contaminants in the Gulf of Maine.
What We Are Doing
The Mussel Watch Program uses an ecosystem-based approach to monitoring, which entails measuring the concentration of chemical contaminants in sediments and the tissues of indigenous bivalves, such as oysters and mussels, as a way to evaluate local environmental quality. Bivalves are used as indicator organisms for chemical pollution because they tend to bioaccumulate contaminants from the large amounts of water they filter, they have limited mobility, and they are found throughout the U.S. coastal zone.
The program currently analyzes sediment and bivalves for both legacy contaminants and CECs. Legacy contaminants, monitored by Mussel Watch since 1986, include compounds such as chlordanes, chlorobenzenes, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), dieldrins, endosulfans, hexachlorocyclohexanes (HCHs), butyltins, PAHs, and PCBs. The monitoring of CECs began in 2009 and includes contaminants such as alkylphenols, alternative flame retardants, current-use pesticides, (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs), polybrominated diphenyl ether (PBDEs), polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), and pharmaceuticals and personal care products. In general, CECs are minimally regulated, not commonly monitored, but potentially toxic chemicals that are finding their way into the environment.
In 2015 and 2016, Mussel Watch analyzed sediment and mussel (Mytilus edulis) samples from a network of 41 sites in the Gulf of Maine for metals, legacy contaminants, and CECs. The network consisted of sites in the Mussel Watch Program and the Gulfwatch Contaminants Monitoring Program and covered coastlines from from Nova Scotia to Massachusetts. Site selection was conducted in collaboration with resources managers from the Gulf of Maine Council on the Marine Environment and involved a strategic mixture of sites that met both programs’ monitoring needs. Mussel Watch designed the 2015/2016 Gulf of Maine chemical stressors survey in collaboration with the Gulfwatch Contaminants Monitoring Program.
Benefits of Our Work
This study supplies much-needed data to the national Mussel Watch Program and local stakeholders and managers in the Gulf of Maine and informs water quality data used by coastal resource managers to develop effective, long-term policies to protect ecosystem services provided by the Gulf of Maine.